Magnetic tides in atmosphere and ocean driven by moon
Both Earth’s oceans and upper atmosphere produce electric current and electromagnetic (EM) fields. Tides caused by the gravitational interaction between the Earth, the Sun and the Moon create reliable, easily constrained electromagnetic signals in both the ocean and upper atmosphere. Geophysicists are interested in using these ocean tidal electromagnetic signals to study the electrical conductivity of Earth’s interior—however, this requires a solid understanding of the upper atmosphere’s contribution to the electromagnetic signal. This study uses a physics-based model to estimate the relative electromagnetic tidal signals of the ocean versus the upper atmosphere to immediately address this concern. We also compare the model predictions with the electromagnetic tidal signals constrained from 64 global observatories. Considering the level of complexity of the upper atmosphere’s electromagnetic tidal signals, we find remarkable agreement between the observed and modeled electromagnetic tidal signals. Some of the discrepancies may be of interest to those in upper atmospheric / space physics because they may be due to unmodeled physical processes. Our results are also very encouraging for geophysicists aiming to use electromagnetic tidal signals to study Earth’s interior since they suggest a small upper atmosphere contribution to the electromagnetic tidal signal generally used.
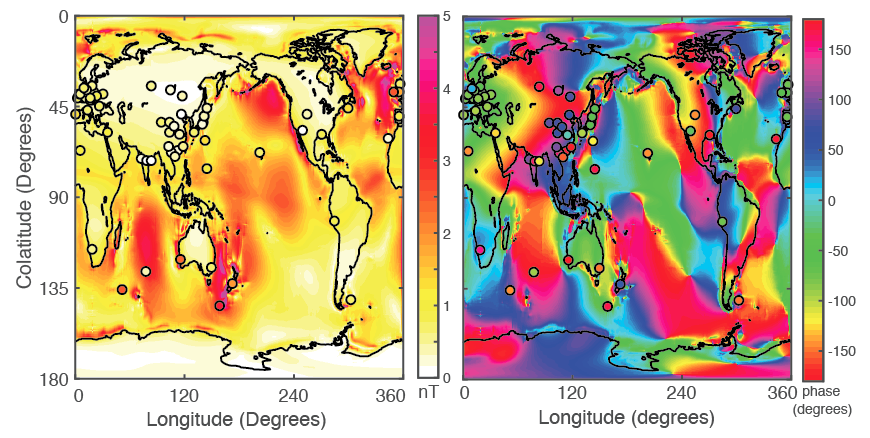
The background map illustrates the total scalar M2 magnetic field amplitude (left) and phase (right) predicted from the sum of the ionosphere and ocean sources. Each colored dot represents the total M2 scalar field amplitude (left) and phase (right) at a geomagnetic observatory (Reproduced from Schnepf et al., 2018).
Methodology and discussion of results in:
Schnepf, N. R., M. Nair, A. Maute, N. M. Pedatella, A. Kuvshinov, A. D. Richmond (2018). A comparison of model-based ionospheric and ocean tidal magnetic signals with observatory data. Geophysical Research Letters. (doi: 10.1029/2018GL078487)
Relevant codes available on Github here.
Grids of the ionospheric and oceanic M2 tidal magnetic fields predicted at sea level:
| Download Ionospheric-Oceanic M2 Simulation (IOMS) Data |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Format | Mbyte | Contents | |
|
Text |
0.002 |
The readme. |
||
| Data | .csv | 0.574 | iono_Fi (180x360): the imaginary part of F calculated from the sealevel ionospheric M2 prediction. | |
| Data | .csv | 0.574 | iono_Fr (180x360): the real part of F calculated from the sealevel ionospheric M2 prediction. | |
| Data | .csv | 0.552 | iono_pi (180x360): The imaginary part of the ionospheric M2 predicted phi component | |
| Data | .csv | 0.550 | iono_pr (180x360): The real part of the ionospheric M2 predicted phi component | |
| Data | .csv | 0.592 | iono_ri (180x360): The imaginary part of the ionospheric M2 predicted radial component | |
| Data | .csv | 0.594 | iono_rr (180x360): The real part of the ionospheric M2 predicted radial component | |
| Data | .csv | 0.556 | iono_ti (180x360): The imaginary part of the ionospheric M2 predicted theta component | |
| Data | .csv | 0.555 | iono_tr (180x360): The real part of the ionospheric M2 predicted theta component | |
| Data | .csv | 9.0 | ocean_Fi (720x1440): the imaginary part of F calculated from the sealevel oceanic M2 prediction | |
| Data | .csv | 8.9 | ocean_Fr (720x1440): the real part of F calculated from the sealevel oceanic M2 prediction | |
| Data | .csv | 9.1 | ocean_pi (720x1440): The imaginary part of the oceanic M2 predicted phi component | |
| Data | .csv | 9.0 | ocean_pr (720x1440): The real part of the oceanic M2 predicted phi component | |
| Data | .csv | 9.0 | ocean_ri (720x1440): The imaginary part of the oceanic M2 predicted radial component | |
| Data | .csv | 8.9 | ocean_rr (720x1440): The real part of the oceanic M2 predicted radial component | |
| Data | .csv | 9.0 | ocean_ti (720x1440): The imaginary part of the oceanic M2 predicted theta component | |
| Data | .csv | 9.0 | ocean_tr (720x1440): The real part of the oceanic M2 predicted theta component | |
